
CFD Trading Basics: Contract for Difference (CFD) trading has become a popular way for many people to participate in financial markets.
This form of trading involves speculating on the price movements of various assets without actually owning the underlying asset. Understanding the basics and benefits of CFD trading can help individuals decide if it aligns with their financial goals and trading style.
A Contract for Difference is a financial derivative that allows traders to speculate on the price movement of an asset, such as stocks, indices, commodities, currencies, or cryptocurrencies. When trading CFDs, the trader enters into an agreement with a broker to exchange the difference in value of an asset from the time the contract is opened to the time it is closed.
Unlike traditional stock trading, there is no need to physically buy or sell the asset. This means traders can focus solely on the movement of prices, whether up or down.
Flexibility in Trading
One of the key benefits of CFD trading is the ability to take advantage of both rising and falling markets. If a trader believes the price of an asset will increase, they can open a long position. Conversely, if they expect the price to decline, they can open a short position.
This flexibility allows market participation in a variety of conditions, offering a broader range of trading possibilities compared to traditional investing where profit is typically only made when prices rise.
CFD trading offers access to a vast array of markets all from a single account. Traders can explore multiple asset classes including equities, commodities like oil and gold, major and minor currency pairs, as well as global indices. This diversity enables portfolio diversification within one platform, which can help manage exposure and spread risk more effectively.
Leverage and Margin
CFD trading commonly involves the use of leverage, meaning traders can open larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. This amplifies the potential effect of price movements on the trading account.
While leverage can magnify gains, it also increases the potential for losses, making it crucial for traders to understand how to manage risk properly. The use of margin means that only a fraction of the total trade value is required to open a position, enhancing capital efficiency and freeing up funds for other trades or investments.

No Ownership, No Physical Delivery
Since CFDs are derivatives, traders do not own the underlying asset. This means there is no need to worry about storage, delivery, or transfer of physical assets such as commodities or shares.
For example, trading CFDs on commodities like gold or oil removes the logistical challenges of buying and storing the actual commodity. This simplifies the trading process and reduces associated costs.
Lower Transaction Costs
Compared to traditional investing, CFD trading often has lower transaction costs. There are generally no stamp duties or additional fees for ownership transfers. Brokers typically make their earnings through spreads or commissions, which can be competitive depending on the platform.
This cost-effectiveness makes CFD trading accessible to a wider audience, including traders who prefer to make frequent or smaller trades.
Ability to Trade on Margin
Trading on margin allows traders to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of money deposited as collateral. This can increase the efficiency of capital use, enabling traders to diversify their strategies across multiple markets without tying up excessive funds.
However, margin trading requires careful management due to the increased risk of losses that can exceed the initial deposit if the market moves unfavorably.
Quick Execution and Market Access
CFD trading platforms typically offer fast trade execution and 24-hour access to global markets, depending on the asset class. This allows traders to act promptly on market developments without delays associated with traditional stock exchanges.
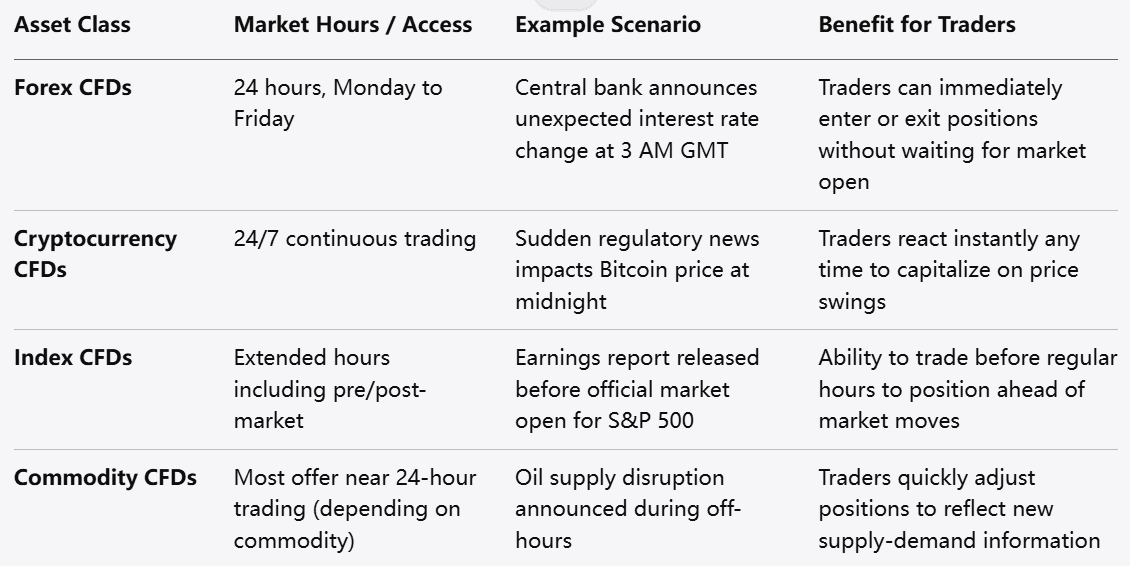
The ability to trade nearly around the clock means traders can respond to news events and price movements in real time, potentially enhancing their ability to capitalize on short-term market fluctuations.
Transparent Pricing and Real-Time Data
Most CFD platforms provide transparent pricing and real-time market data, which helps traders make informed decisions. The availability of live quotes, charts, and news feeds ensures users can monitor market conditions closely and adjust their strategies accordingly.
This transparency builds trust in the trading environment and enables active engagement with markets.
Hedging Capabilities
CFD trading can be used as a hedging tool to protect existing portfolios. For example, if a trader holds shares in a particular company but expects a short-term decline in its value, they might open a CFD short position on the same stock to offset potential losses.
This ability to hedge enables better risk management and can help mitigate the impact of adverse market movements.
No Expiry Dates
Unlike some derivative instruments, CFDs generally do not have fixed expiry dates. Positions can be held as long as the trader desires, provided margin requirements are met.
This flexibility allows traders to maintain exposure to markets for periods ranging from seconds to months, depending on their strategy and market conditions.

CFD brokers usually offer intuitive platforms with a range of tools designed to cater to both beginners and experienced traders. Features often include customizable charts, order types, and educational resources.
This ease of use lowers the barrier to entry and encourages individuals to explore trading without needing extensive prior knowledge.
CFD trading offers a versatile way to participate in financial markets by speculating on price movements without owning the underlying assets. Its flexibility to trade upward or downward trends, access to diverse markets, and efficient use of capital through leverage makes it an appealing choice for many.
Additionally, the ability to hedge, lower transaction costs, and no requirement for physical delivery contribute to its advantages. However, understanding the risks associated with leverage and market volatility is essential before engaging in CFD trading.
By exploring and mastering these basics, individuals can determine if CFD trading fits their approach to financial markets.
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.