
Crypto market analysis: Cryptocurrency has become a widely discussed topic in financial circles and beyond.
To understand its impact and how it functions, it’s important to explore what cryptocurrency is, what it enables users to do, its market features, and the structure of the market itself. This guide breaks down these aspects and provides clarity on this evolving digital landscape.
Cryptocurrency is a form of digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security. Unlike traditional money issued by governments and central banks, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology. This technology ensures transparency and security by recording transactions on a distributed ledger that is maintained by numerous participants worldwide.
Because cryptocurrencies are digital, they do not have a physical form like coins or banknotes. Instead, they exist solely in electronic form and are accessible through digital wallets. The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies means no single authority controls them, making them resistant to censorship and centralized control.

Cryptocurrency offers a range of possibilities beyond just being a form of currency. Some common uses include:
The cryptocurrency market has several distinguishing features that set it apart from traditional financial markets:
Decentralization: Most cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks, removing the need for central authorities and intermediaries.
24/7 Market: Unlike traditional stock or commodity markets, the cryptocurrency market operates continuously without closing hours, allowing trading at any time.
High Volatility: Price movements in cryptocurrencies tend to be more volatile compared to many traditional assets, often resulting in rapid changes within short periods.
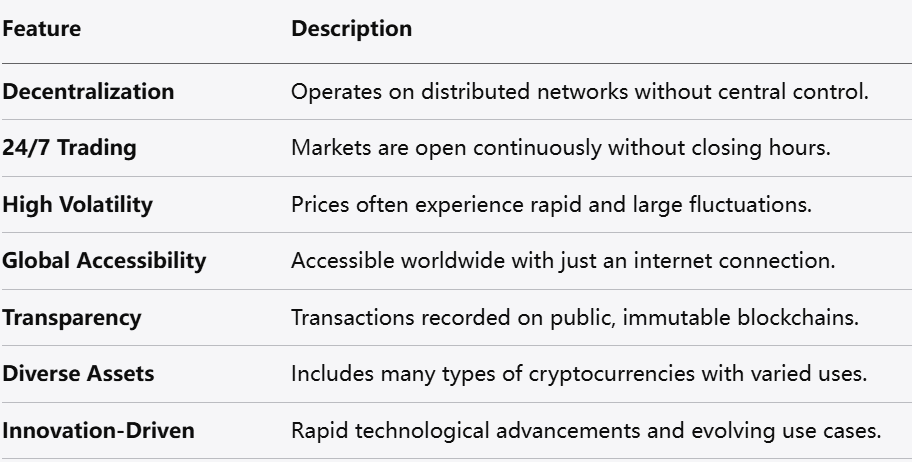
Global Accessibility: Anyone with internet access can participate in the cryptocurrency market regardless of geographic location or banking access.
Transparency and Immutability: Transactions are recorded on public blockchains that are transparent and cannot be altered once confirmed, enhancing trust in the system.
Variety of Assets: The market includes thousands of different cryptocurrencies, each with unique features, purposes, and technological foundations.
Innovation-Driven: The sector is characterized by rapid technological development and the emergence of new use cases, making it a dynamic and evolving space.
The cryptocurrency market can be broadly classified into several categories based on use cases, technology, and market behavior:
Payment Coins: These cryptocurrencies primarily serve as a means of exchange or digital cash, facilitating peer-to-peer payments.
Utility Tokens: These provide access to specific services or platforms, often functioning within decentralized applications or ecosystems.
Security Tokens: Representing ownership or rights to an asset, these tokens mirror traditional securities and are often subject to regulatory oversight.
Stablecoins: Designed to maintain a stable value by being pegged to fiat currencies or other assets, stablecoins offer reduced volatility compared to other cryptocurrencies.
Privacy Coins: Focused on enhancing transaction privacy and anonymity, these cryptocurrencies implement advanced cryptographic techniques to conceal transaction details.
DeFi Tokens: Used within decentralized finance protocols, these tokens enable various financial services without central intermediaries.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): Unique digital assets representing ownership of collectibles, art, or other distinct items, which cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis like traditional cryptocurrencies.
Each category serves different purposes and appeals to diverse user needs, adding depth and complexity to the overall market.

Cryptocurrency represents a transformative development in the world of digital finance. As a decentralized form of digital currency secured by cryptography and blockchain technology, it offers a wide array of functions ranging from payments and asset ownership to programmable contracts and decentralized financial services.
The cryptocurrency market stands out for its continuous operation, global accessibility, and diverse assets. Its decentralized nature and transparency provide a new framework for exchanging value and conducting financial activities outside traditional systems.
Understanding the classifications within the market helps clarify the roles different cryptocurrencies play, whether as mediums of exchange, utility tokens, or digital collectibles. As the market continues to evolve, it remains an area of keen interest for those exploring new models of digital interaction and finance.
Q: How is cryptocurrency different from traditional money?
A: Cryptocurrency is digital and decentralized, operating without central banks or governments, while traditional money is issued and regulated by national authorities.
Q: Can cryptocurrencies be used for everyday purchases?
A: In some cases, yes. Increasing numbers of merchants accept cryptocurrencies as payment, though adoption varies by region and service.
Q: What makes cryptocurrency transactions secure?
A: Transactions are recorded on blockchain ledgers using cryptography, making them tamper-resistant and transparent.
Q: Are all cryptocurrencies the same?
A: No, cryptocurrencies vary widely in purpose, technology, and design, ranging from payment coins to specialized tokens for various applications.
Q: Can anyone trade cryptocurrencies?
A: Generally, yes. Access to the market requires only an internet connection and a digital wallet, though regulations may differ by jurisdiction.
This overview highlights the foundational aspects of cryptocurrency and its market, providing a clear understanding of what makes this digital asset class unique and how it functions in today’s financial landscape.
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.