
What is forex trading: Forex trading involves exchanging one currency for another in the global marketplace.
It is a decentralized market where currencies are traded continuously, allowing participants to seek gains from the fluctuations in exchange rates. Understanding how to navigate this market effectively requires knowledge, discipline, and a well-developed approach.
Trading currencies involves buying a currency pair if you anticipate the base currency will strengthen compared to the quote currency, or selling if you expect the opposite. The forex market operates 24 hours a day, providing ample opportunities to engage, but it also demands careful planning and strategy.
A well-structured trading strategy is essential for navigating the complexities of the forex market. Without a clear plan, decisions are often driven by emotion or guesswork, which can lead to erratic outcomes. A strategy helps to:
Forex trading strategies generally fall into three broad categories:
2.1 Trend-Following Strategies
These strategies seek to capitalize on sustained price movements in a particular direction. Traders identify trends and attempt to ride them until signs of reversal appear.
2.2 Range-Bound Strategies
When the market moves sideways between established support and resistance levels, range-bound strategies aim to buy near support and sell near resistance.
2.3 Breakout Strategies
Breakout strategies focus on moments when price moves beyond established ranges, signaling potential new trends or volatility bursts.
Each category suits different market environments and trader preferences, and many combine elements from each to enhance adaptability.

Here are seven widely used approaches that can help provide structure for trading decisions:
3.1 The EMA Crossover Strategy
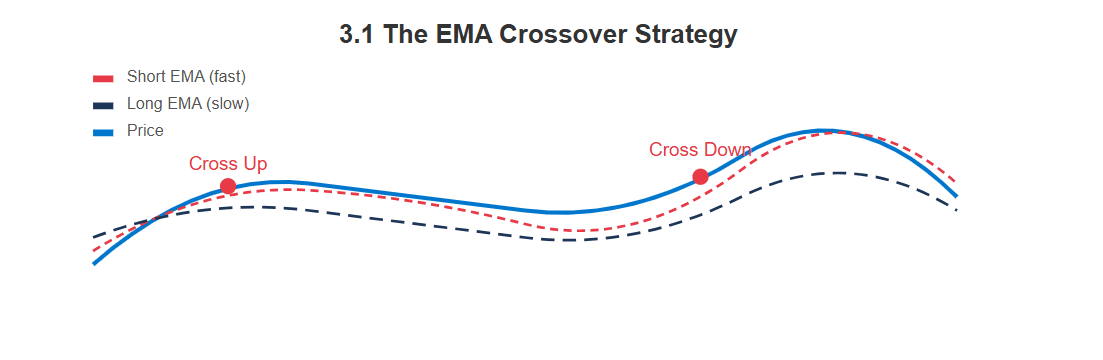
This method uses two exponential moving averages (EMAs) of different lengths. When the shorter-term EMA crosses above the longer-term EMA, it signals a potential upward move. Conversely, a crossover below suggests a downward move. It helps identify trend changes early.
3.2 Gann Trend Following Strategy
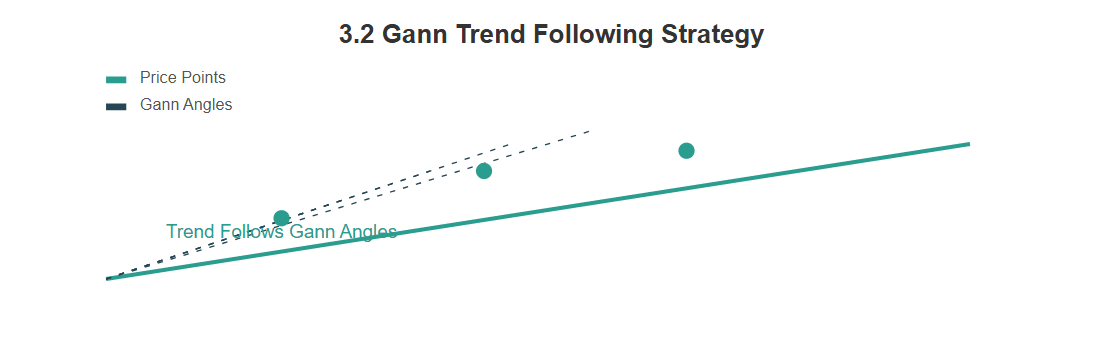
Inspired by the work of W.D. Gann, this strategy focuses on identifying long-term trends and trading in their direction. It often uses geometric angles and time cycles to gauge momentum and potential turning points.
3.3 Support and Resistance Strategy
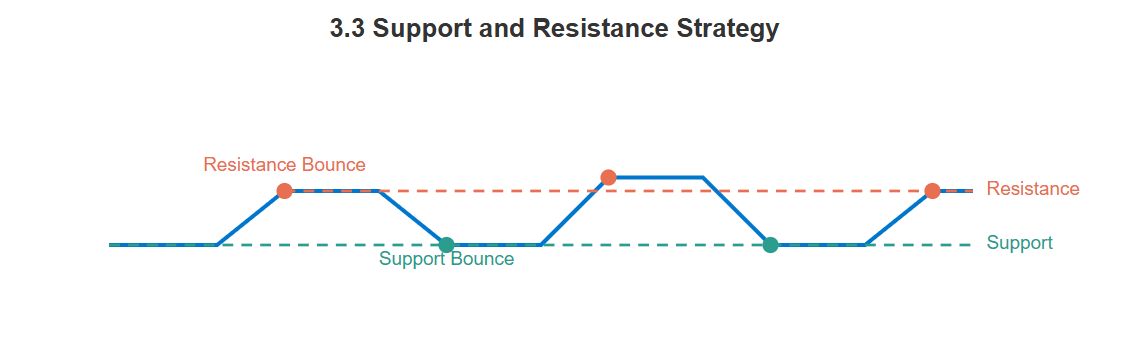
This approach centers on price levels where currency pairs have historically reversed or paused. Traders watch these levels closely to enter or exit trades, expecting the price to react similarly in the future.
3.4 Pinbar Strategy
The pinbar is a candlestick pattern characterized by a long wick and small body, indicating rejection of certain price levels. It signals potential reversals and is often used in conjunction with support and resistance areas.
3.5 Bollinger Bounce Strategy
This strategy relies on Bollinger Bands, which envelope price with upper and lower bands based on volatility. The bounce strategy anticipates price will revert to the mean after touching a band, offering entry points near extremes.
3.6 Bollinger Breakout Strategy
In contrast to the bounce, this strategy looks for price to break beyond the Bollinger Bands, suggesting a strong directional move. Traders enter trades anticipating continuation in the breakout direction.
3.7 The London Breakout Strategy
This method takes advantage of increased activity during the London market open, often characterized by higher volatility and volume. Traders look for breakouts from the overnight range to capture early momentum.
To make any trading strategy work effectively, it is important to adhere to certain principles:
Stick to Your Plan: Avoid deviating from your strategy based on emotion or external noise. Consistency is key.
Risk Management: Always define how much you are willing to risk on each trade to protect capital.
Keep Records: Maintain a trading journal to review decisions, learn from mistakes, and refine your approach.
Avoid Overtrading: Trade only when your strategy signals a clear setup; resist the urge to chase the market.
Adapt to Market Conditions: Markets evolve, so be prepared to adjust your strategy if conditions change.
Use Stop-Losses: Protect yourself from unexpected adverse moves by setting limits on potential losses.
Maintain Patience: Good setups don’t occur constantly; waiting for the right moment often leads to better outcomes.
Continuous Learning: Stay informed and open to improving your knowledge and skills over time.
Forex trading offers a dynamic environment where currency values fluctuate based on numerous factors, providing chances to engage and navigate the market. Using a clear trading strategy is fundamental to approaching this market with discipline and structure. Whether following trends, trading ranges, or capitalizing on breakout moves, selecting an appropriate method tailored to one’s style and market conditions is important.
Combining strategic approaches with sound risk management and disciplined execution can enhance consistency and help manage the challenges of trading. Remaining patient, adaptable, and committed to ongoing learning also supports steady progress in understanding and interacting with the forex market.
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.